31st World Chess Problem Solving Championship
The World Chess Problem Solving Championship took place in Rhodes, Greece, on
16th-17th October 2007. This was one of the strongest solving championships ever
held; in addition to defending champion Piotr Murdzia, the former world champions
Ofer Comay, Michel Caillaud, Michael Pfannkuche, Georgi Evseev, Arno Zude, Noam
Elkies, Jonathan Mestel, Jorma Paavilainen, Andrey Selivanov and John Nunn were
also taking part.
The world championship consists of six timed papers, each consisting of three
problems or studies. The six papers cover two-movers, three-movers, studies,
helpmates, moremovers (mates in more than three moves) and selfmates. Five points
are awarded for each position, according to how complete the solver’s
solution is, so 15 points is the maximum score for each of the six rounds.
At the end of the first day, with three rounds completed, Mestel, Comay and
Murdzia had a perfect score, while Evseev had dropped half a point. Nunn was
slightly further behind with 44 points out of a possible 45.
The second day’s problems are generally more testing than those on the
first day, but in the first round of the day the favourites generally did well.
Mestel, Comay, Evseev and Nunn all scored a maximum, but Murdzia dropped two
points to fall behind.
However, the second round of the day, the moremovers, devastated the field.
Evseev dropped four points and Comay a massive eight. The biggest shock was
that Jonathan Mestel scored no points at all in the moremovers. Afterwards,
he explained that instead of just concentrating on one problem and making sure
that he got five points, he jumped from one to another and ended up not solving
any of them. All solvers know that such a disaster is never far away when there
is a difficult round.

The winners: Georgy Evseev, John Nunn and Piotr Murdzia
This round proved decisive in that John Nunn managed a perfect score, and at
a stroke he overtook all his rivals and established a clear lead. In the last
round, the selfmates, Murdzia and Comay managed a perfect score, but it was
to no avail since Nunn did likewise, maintaining his lead. The final leading
scores were: Nunn 89, Evseev 83.5, Murdzia 83, Comay 82, Zude 75, Tummes 73
(82 participants). When we asked John about his incredible 89/90 score he replied
dryly: "Well, that leaves room for improvement."
| No. |
SOLVER |
|
#2 |
#3 |
Endgames |
H# |
#n |
S# |
Total |
| |
|
|
pts |
time |
pts |
time |
pts |
time |
pts |
time |
pts |
time |
pts |
time |
pts |
time |
| |
|
max. |
15 |
20 |
15 |
60 |
15 |
100 |
15 |
50 |
15 |
80 |
15 |
50 |
90 |
360 |
| 1 |
John Nunn |
GBR |
15 |
17 |
14,0 |
53 |
15,0 |
46 |
15,0 |
50 |
15,0 |
61 |
15,0 |
46 |
89,0 |
273 |
| 2 |
Georgy Evseev |
RUS |
15 |
20 |
15,0 |
60 |
14,5 |
62 |
15,0 |
32 |
11,0 |
80 |
13,0 |
50 |
83,5 |
304 |
| 3 |
Piotr Murdzia |
POL |
15 |
20 |
15,0 |
59 |
15,0 |
80 |
13,0 |
50 |
10,0 |
80 |
15,0 |
49 |
83,0 |
338 |
| 4 |
Ofer Comay |
ISR |
15 |
18 |
15,0 |
58 |
15,0 |
36 |
15,0 |
24 |
7,0 |
80 |
15,0 |
36 |
82,0 |
252 |
| 5 |
Arno Zude |
GER |
15 |
17 |
15,0 |
59 |
12,0 |
100 |
10,0 |
50 |
8,0 |
80 |
15,0 |
50 |
75,0 |
356 |
| 6 |
Boris Tummes |
GER |
15 |
20 |
13,5 |
60 |
14,5 |
100 |
13,0 |
50 |
12,0 |
80 |
5,0 |
50 |
73,0 |
360 |
| 7 |
Andrey Selivanov |
RUS |
15 |
20 |
8,5 |
60 |
10,5 |
100 |
15,0 |
25 |
13,0 |
80 |
10,0 |
49 |
72,0 |
334 |
| 8 |
Michael Pfannkuche |
GER |
15 |
20 |
15,0 |
49 |
13,5 |
86 |
8,5 |
50 |
11,0 |
80 |
9,0 |
50 |
72,0 |
335 |
| 9 |
Volodimir Pogorelov |
UKR |
15 |
20 |
13,5 |
60 |
15,0 |
71 |
13,0 |
50 |
0,0 |
80 |
15,0 |
50 |
71,5 |
331 |
| 10 |
Noam Elkies |
ISR |
15 |
20 |
14,0 |
60 |
15,0 |
74 |
7,5 |
50 |
4,5 |
80 |
15,0 |
50 |
71,0 |
334 |
| 11 |
Vladimir Podinic |
SRB |
15 |
20 |
14,5 |
60 |
15,0 |
70 |
13,0 |
50 |
3,0 |
80 |
10,0 |
50 |
70,5 |
330 |
| 12 |
Eddy Van Beers |
BEL |
15 |
20 |
5,0 |
60 |
15,0 |
70 |
10,5 |
50 |
11,0 |
80 |
13,0 |
50 |
69,5 |
330 |
| 13 |
Alexander Feoktistov |
RUS |
15 |
19 |
10,0 |
60 |
13,5 |
100 |
8,0 |
50 |
11,5 |
76 |
11,0 |
50 |
69,0 |
355 |
| 14 |
Kari Karhunen |
FIN |
15 |
20 |
13,5 |
60 |
12,0 |
98 |
13,0 |
50 |
1,0 |
80 |
14,0 |
50 |
68,5 |
358 |
| 15 |
Aleksandr Bulavka |
BLR |
15 |
20 |
8,0 |
60 |
15,0 |
72 |
13,0 |
50 |
5,0 |
80 |
12,0 |
50 |
68,0 |
332 |
| 16 |
Jonathan Mestel |
GBR |
15 |
20 |
15,0 |
60 |
15,0 |
74 |
15,0 |
50 |
0,0 |
80 |
8,0 |
50 |
68,0 |
334 |
| 17 |
Valery Kopyl |
UKR |
15 |
20 |
8,0 |
60 |
15,0 |
95 |
15,0 |
41 |
1,0 |
80 |
12,0 |
50 |
66,0 |
346 |
| 18 |
Hans Uitenbroek |
NLD |
15 |
17 |
9,0 |
60 |
11,0 |
100 |
13,0 |
50 |
6,0 |
80 |
11,0 |
50 |
65,0 |
357 |
| 19 |
Mikheil Gabeskiria |
GEO |
15 |
20 |
8,5 |
60 |
15,0 |
84 |
8,0 |
50 |
8,0 |
80 |
10,0 |
50 |
64,5 |
344 |
| 20 |
Andrey Petrov |
RUS |
15 |
20 |
13,5 |
60 |
6,5 |
89 |
11,0 |
50 |
8,0 |
80 |
10,0 |
50 |
64,0 |
349
|
Nunn’s score was unusually high and his winning margin was also exceptional.
This is the second time he has been world champion, the previous occasion being
in 2004. In 2005 and 2006 he finished third.
The World Chess Solving Championship also functions as an event for national
teams, and operates by combining the scores from each country’s three
solvers. Great Britain had previously won the team event in 2005 and 2006, and
this year they repeated their success, based substantially on Nunn’s individual
score. The leading countries were: Great Britain 163, Russia 158.5, Germany
158, Israel 155.5, Poland 153.5, Serbia 143.5. The other two British solvers
were Jonathan Mestel and David Friedgood.
| No. |
SOLVER |
#2 |
#3 |
Endgames |
H# |
#n |
S# |
Total |
| |
|
pts |
time |
pts |
time |
pts |
time |
pts |
time |
pts |
time |
pts |
time |
pts |
time |
| |
max (indiv.) |
15 |
20 |
15 |
60 |
15 |
100 |
15 |
50 |
15 |
80 |
15 |
50 |
90 |
360 |
| |
max (team) |
30 |
40 |
30 |
120 |
30 |
200 |
30 |
100 |
30 |
160 |
30 |
100 |
180 |
720 |
| 1 |
GREAT BRITAIN |
30 |
36 |
29,0 |
113 |
30,0 |
120 |
30,0 |
100 |
19,0 |
141 |
25,0 |
96 |
163,0 |
606 |
| 1 |
John Nunn |
15 |
17 |
14,0 |
53 |
15,0 |
46 |
15,0 |
50 |
15,0 |
61 |
15,0 |
46 |
89,0 |
273 |
| 16 |
Jonathan Mestel |
15 |
20 |
15,0 |
60 |
15,0 |
74 |
15,0 |
50 |
0,0 |
80 |
8,0 |
50 |
68,0 |
334 |
| 39 |
David Friedgood |
15 |
19 |
5,0 |
60 |
14,5 |
86 |
5,0 |
50 |
4,0 |
80 |
10,0 |
50 |
53,5 |
345 |
| 2 |
RUSSIA |
30 |
40 |
23,5 |
120 |
25,0 |
162 |
30,0 |
57 |
24,0 |
160 |
26,0 |
100 |
158,5 |
639 |
| 2 |
Georgy Evseev |
15 |
20 |
15,0 |
60 |
14,5 |
62 |
15,0 |
32 |
11,0 |
80 |
13,0 |
50 |
83,5 |
304 |
| 7 |
Andrey Selivanov |
15 |
20 |
8,5 |
60 |
10,5 |
100 |
15,0 |
25 |
13,0 |
80 |
10,0 |
49 |
72,0 |
334 |
| 33 |
Alexandr Azhusin |
15 |
20 |
5,0 |
60 |
8,0 |
100 |
11,0 |
50 |
8,0 |
80 |
13,0 |
50 |
60,0 |
360 |
| 3 |
GERMANY |
30 |
37 |
30,0 |
108 |
28,0 |
186 |
23,0 |
100 |
23,0 |
160 |
24,0 |
100 |
158,0 |
691 |
| 6 |
Boris Tummes |
15 |
20 |
13,5 |
60 |
14,5 |
100 |
13,0 |
50 |
12,0 |
80 |
5,0 |
50 |
73,0 |
360 |
| 5 |
Arno Zude |
15 |
17 |
15,0 |
59 |
12,0 |
100 |
10,0 |
50 |
8,0 |
80 |
15,0 |
50 |
75,0 |
356 |
| 8 |
Michael Pfannkuche |
15 |
20 |
15,0 |
49 |
13,5 |
86 |
8,5 |
50 |
11,0 |
80 |
9,0 |
50 |
72,0 |
335 |
| 4 |
ISRAEL |
30 |
33 |
29,0 |
118 |
30,0 |
110 |
25,0 |
74 |
11,5 |
160 |
30,0 |
86 |
155,5 |
581 |
| 10 |
Noam Elkies |
15 |
20 |
14,0 |
60 |
15,0 |
74 |
7,5 |
50 |
4,5 |
80 |
15,0 |
50 |
71,0 |
334 |
| 4 |
Ofer Comay |
15 |
18 |
15,0 |
58 |
15,0 |
36 |
15,0 |
24 |
7,0 |
80 |
15,0 |
36 |
82,0 |
252 |
| 38 |
Mark Erenburg |
15 |
15 |
8,5 |
60 |
9,0 |
98 |
10,0 |
50 |
2,5 |
80 |
10,0 |
50 |
55,0 |
353 |
| 5 |
POLAND |
30 |
40 |
25,0 |
119 |
30,0 |
137 |
21,5 |
100 |
22,0 |
160 |
25,0 |
99 |
153,5 |
655 |
| 3 |
Piotr Murdzia |
15 |
20 |
15,0 |
59 |
15,0 |
80 |
13,0 |
50 |
10,0 |
80 |
15,0 |
49 |
83,0 |
338 |
| 31 |
Bogusz Piliczewski |
15 |
20 |
9,0 |
60 |
11,5 |
100 |
8,0 |
50 |
12,0 |
80 |
5,0 |
50 |
60,5 |
360 |
| 25 |
Jacek Stopa |
15 |
20 |
10,0 |
60 |
15,0 |
57 |
8,5 |
50 |
3,5 |
80 |
10,0 |
50 |
62,0 |
317 |
| 6 |
SERBIA |
30 |
37 |
29,5 |
106 |
23,5 |
162 |
28,0 |
98 |
12,5 |
160 |
20,0 |
98 |
143,5 |
661 |
| 32 |
Marjan Kovacevic |
15 |
17 |
15,0 |
46 |
8,0 |
100 |
13,0 |
50 |
4,0 |
80 |
5,0 |
50 |
60,0 |
343 |
| 26 |
Milan Velimirovic |
15 |
20 |
5,0 |
60 |
8,5 |
92 |
15,0 |
48 |
8,5 |
80 |
10,0 |
48 |
62,0 |
348 |
| 11 |
Vladimir Podinic |
15 |
20 |
14,5 |
60 |
15,0 |
70 |
13,0 |
50 |
3,0 |
80 |
10,0 |
50 |
70,5 |
330 |
| 7 |
UKRAINE |
30 |
40 |
21,5 |
120 |
30,0 |
166 |
28,0 |
91 |
5,0 |
160 |
27,0 |
100 |
141,5 |
677 |
| 17 |
Valery Kopyl |
15 |
20 |
8,0 |
60 |
15,0 |
95 |
15,0 |
41 |
1,0 |
80 |
12,0 |
50 |
66,0 |
346 |
| 9 |
Volodimir Pogorelov |
15 |
20 |
13,5 |
60 |
15,0 |
71 |
13,0 |
50 |
0,0 |
80 |
15,0 |
50 |
71,5 |
331 |
| 57 |
Sergey Borodavkin |
10 |
20 |
5,0 |
60 |
9,0 |
100 |
5,0 |
50 |
4,0 |
80 |
11,0 |
50 |
44,0 |
360 |
| 8 |
FINLAND |
25 |
40 |
27,5 |
120 |
26,5 |
195 |
28,0 |
98 |
5,5 |
160 |
27,0 |
100 |
139,5 |
713 |
| 14 |
Kari Karhunen |
15 |
20 |
13,5 |
60 |
12,0 |
98 |
13,0 |
50 |
1,0 |
80 |
14,0 |
50 |
68,5 |
358 |
| 52 |
Jorma Paavilainen |
5 |
20 |
10,0 |
60 |
3,5 |
100 |
15,0 |
48 |
1,0 |
80 |
13,0 |
50 |
47,5 |
358 |
| 24 |
Harri Hurme |
10 |
20 |
14,0 |
60 |
14,5 |
97 |
10,0 |
50 |
4,5 |
80 |
10,0 |
50 |
63,0 |
357 |
| 9 |
NETHERLANDS |
30 |
35 |
18,5 |
120 |
29,5 |
193 |
21,0 |
100 |
15,0 |
160 |
23,0 |
100 |
137,0 |
708 |
| 28 |
Dolf Wissmann |
15 |
18 |
8,5 |
60 |
15,0 |
100 |
3,5 |
50 |
8,0 |
80 |
12,0 |
50 |
62,0 |
358 |
| 46 |
Peter v. d. Heuvel |
0 |
20 |
9,5 |
60 |
14,5 |
93 |
8,0 |
50 |
7,0 |
80 |
11,0 |
50 |
50,0 |
353 |
| 18 |
Hans Uitenbroek |
15 |
17 |
9,0 |
60 |
11,0 |
100 |
13,0 |
50 |
6,0 |
80 |
11,0 |
50 |
65,0 |
357 |
| 10 |
SLOVAKIA |
25 |
39 |
21,0 |
120 |
25,5 |
176 |
23,0 |
100 |
13,0 |
160 |
21,5 |
100 |
129,0 |
695 |
| 34 |
Emil Klemanic |
10 |
20 |
12,5 |
60 |
14,5 |
76 |
5,0 |
50 |
5,0 |
80 |
11,0 |
50 |
58,0 |
336 |
| 29 |
Marek Kolck |
15 |
19 |
5,0 |
60 |
11,0 |
100 |
13,0 |
50 |
8,0 |
80 |
10,0 |
50 |
62,0 |
359 |
| 58 |
Lubomir Sirn |
10 |
20 |
8,5 |
60 |
4,5 |
97 |
10,0 |
50 |
0,0 |
80 |
10,5 |
50 |
43,5 |
357
|
A sample of the problems
Tony Lewis – Chess 1952
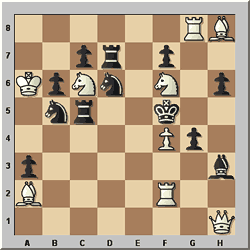
White to play and mate in 2
All Black's available moves are already provided with a white mate,
for example if the b5-knight moves, then Nd4#, or if the d6-knight moves, then
Qe4#. Thus if White had a pure waiting move, then the problem would be solved.
However, there is no pure waiting move, for example 1 Bb3 would give Black the
extra possibility of 1...a2.
M A Karimov – Mladi autori 1952
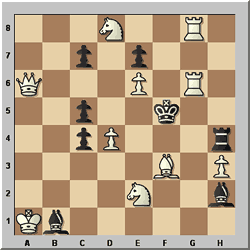
White to play and mate in 3
Here is a more complex problem. In a solving event, to get full marks
you have to not only give the key move, but also all the variations leading
to mate. When there are several variations, it is easy to miss one and thereby
drop a point or half-point.
Walther Jorgensen – Die Schwalbe 1950
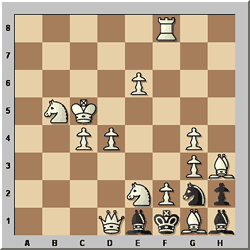
White to play and mate in 4
In this problem, the key move is far from obvious. Black will play
...hxg1 and will have a choice of four promotion pieces; note especially the
choice of a rook, by which Black attempts to stalemate himself. The key idea
is to focus on the most awkward promotion and see if that helps to determine
the key move. The large number of complex variations caused several solvers
to drop points on this problem.
Horst Boettger – Die Welt 1994
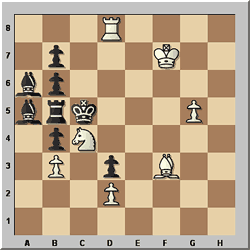
White to play and mate in 6
Although there is only a single line of play, and Black's moves are almost
all forced, this problem defeated a number of solvers, including former champion
Jonathan Mestel. Black is in stalemate, so White's first move must allow the
black king to move. Then, to prevent Black's pieces coming out, White must immediately
force the king back to c5. The question is how White can make progress while
keeping Black bottled up.
Ilja Mikan – Die Schwalbe 1935
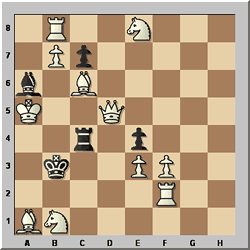
White to play and selfmate in 5
In this problem White must force Black to deliver mate in 5 moves (White
starts). Long selfmates can be very difficult to solve, but a good start is
to spot a possible final mating position. Here Black has only three legal moves,
and after 1...Bxb7 John saw the plausible line 2 something exf3 3 Qd3+ Rc3 4
something Rxd3 5 Bd5+ Rxd5#. The obvious problem here is that there are three
unknown White moves, which have to be used up somehow.
The solutions to the above problems will be provided next week.
Links
The PCCC operates under a mandate from the FIDE, with chess federations or
chess problem societies of 39 countries participating. The task of the Commission
is to pay attention to all matters of international interest in problem chess
and studies within the framework of the FIDE. In particular, its duties include:
1. The dissemination and encouragement of chess composition throughout the
world.
2. The formulation of rules and guide-lines in all spheres of chess composition.
3. The arrangement of official international composing and solving tourneys.
4. The initiation of the publication of collections of general interest, etc.
(FIDE-Albums)
5. The award of titles to especially deserving representatives of chess composition
including solvers, subject to the approval of the FIDE.

This year's Competition director: Brian Stephenson, with his assistants
Peter Bakker, Ward Stoffelen and Neal Turner
John Nunn with his 10-inch Schmidt-Cassegrain telescope at his home in Surrey.
Currently he is watching and worrying about the sudden million-fold brightening
of Comet Holmes, which he attributes to "thermal stress" (the
boring explanation) or to somebody testing an asteroid
buster (much better, John!). But all of this is a story for next
week...

British solvers have recorded a unique hat trick of victories by taking the
gold medals at the World Chess Problem Solving Championship. The competition
was held at the 50th World Congress for Chess Compositions in Rhodes and the
British team was supported by Winton Capital Management whose assistance ensured
the participation of our leading trio of solvers.
John Nunn’s magnificent individual performance was the foundation of
the victory and his score of 89/90 secured his second individual world solving
title ahead of a galaxy of former world champion solvers. Nunn’s team
mates were David Friedgood and Jonathan Mestel and the team total of 163/180
was comfortably ahead of Russia on 158.5 and Germany on 158.
In chess problem solving, points are scored for the accuracy and completeness
of the solutions which are hand written and submitted to the judges. The competition
comprised six rounds and in each round the team’s score was the total
of the best two performers. Each round presented the solvers with a different
task. There were; mates in 2 moves, mates in 3 moves, mates in more than 3 moves,
Endgame Studies, Helpmates; where both sides cooperate to ensure Black is mated,
and Selfmates; where White forces Black to mate him.
































